







The Most Famous
WRITERS from United Kingdom
This page contains a list of the greatest British Writers. The pantheon dataset contains 7,302 Writers, 789 of which were born in United Kingdom. This makes United Kingdom the birth place of the 2nd most number of Writers.
Top 10
The following people are considered by Pantheon to be the top 10 most legendary British Writers of all time. This list of famous British Writers is sorted by HPI (Historical Popularity Index), a metric that aggregates information on a biography's online popularity. Visit the rankings page to view the entire list of British Writers.

1. William Shakespeare (1564 - 1616)
With an HPI of 92.59, William Shakespeare is the most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 230 different languages on wikipedia.
William Shakespeare (c. 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon" or simply "the Bard". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18, he married Anne Hathaway, with whom he had three children: Susanna, and twins Hamnet and Judith. Sometime between 1585 and 1592 he began a successful career in London as an actor, writer, and part-owner ("sharer") of a playing company called the Lord Chamberlain's Men, later known as the King's Men after the ascension of King James VI of Scotland to the English throne. At age 49 (around 1613) he appears to have retired to Stratford, where he died three years later. Few records of Shakespeare's private life survive; this has stimulated considerable speculation about such matters as his physical appearance, his sexuality, his religious beliefs and even certain fringe theories as to whether the works attributed to him were written by others. Shakespeare produced most of his known works between 1589 and 1613. His early plays were primarily comedies and histories and are regarded as some of the best works produced in these genres. He then wrote mainly tragedies until 1608, among them Hamlet, Othello, King Lear and Macbeth, all considered to be among the finest works in English. In the last phase of his life he wrote tragicomedies (also known as romances) such as The Winter's Tale and The Tempest, and collaborated with other playwrights. Many of Shakespeare's plays were published in editions of varying quality and accuracy during his lifetime. However, in 1623 John Heminges and Henry Condell, two fellow actors and friends of Shakespeare's, published a more definitive text known as the First Folio, a posthumous collected edition of Shakespeare's dramatic works that includes 36 of his plays. Its preface includes a prescient poem by Ben Jonson, a former rival of Shakespeare, who hailed Shakespeare with the now-famous epithet: "not of an age, but for all time".

2. Agatha Christie (1890 - 1976)
With an HPI of 85.80, Agatha Christie is the 2nd most famous British Writer. Her biography has been translated into 141 different languages.
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan (née Miller; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976), was an English author known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving around fictional detectives Hercule Poirot and Miss Marple. She is widely regarded as one of the greatest writers, particularly in the mystery genre. A writer during the "Golden Age of Detective Fiction", Christie has been called the "Queen of Crime"—a nickname now trademarked by her estate—or the "Queen of Mystery". She wrote the world's longest-running play, the murder mystery The Mousetrap, which has been performed in the West End of London since 1952. She also wrote six novels under the pseudonym Mary Westmacott. In 1971, she was made a Dame (DBE) by Queen Elizabeth II for her contributions to literature. She is the best-selling fiction writer of all time, her novels having sold more than two billion copies. Christie was born into a wealthy upper-middle-class family in Torquay, Devon, and was largely home-schooled. She was initially an unsuccessful writer with six consecutive rejections, but this changed in 1920 when The Mysterious Affair at Styles, featuring detective Hercule Poirot, was published. Her first husband was Archibald Christie; they married in 1914 and had one child before divorcing in 1928. Following the breakdown of her marriage and the death of her mother in 1926, she made international headlines by going missing for eleven days. During both world wars, she served in hospital dispensaries, acquiring a thorough knowledge of the poisons that featured in many of her novels, short stories, and plays. Following her marriage to archaeologist Max Mallowan in 1930, she spent several months each year on archaeological excavations in the Middle East and used her first-hand knowledge of this profession in her fiction. According to UNESCO's Index Translationum, she remains the most-translated individual author. Her novel And Then There Were None is one of the top-selling books of all time, with approximately 100 million copies sold. Christie's stage play The Mousetrap holds the world record for the longest initial run. It opened at the Ambassadors Theatre in the West End on 25 November 1952, and by 2018 there had been more than 27,500 performances. The play was temporarily closed in 2020 because of COVID-19 lockdowns in London before it reopened in 2021. In 1955, Christie was the first recipient of the Mystery Writers of America's Grand Master Award. Later that year, Witness for the Prosecution received an Edgar Award for best play. In 2013, she was voted the best crime writer and The Murder of Roger Ackroyd the best crime novel ever by 600 professional novelists of the Crime Writers' Association. In 2015, And Then There Were None was named the "World's Favourite Christie" in a vote sponsored by the author's estate. Many of Christie's books and short stories have been adapted for television, radio, video games, and graphic novels. More than 30 feature films are based on her work.

3. H. G. Wells (1866 - 1946)
With an HPI of 85.76, H. G. Wells is the 3rd most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 112 different languages.
Herbert George Wells (21 September 1866 – 13 August 1946) was an English writer, prolific in many genres. He wrote more than forty novels and dozens of short stories. His non-fiction output included works of social commentary, politics, history, popular science, satire, biography, and autobiography. Wells is most known today for his groundbreaking science fiction novels; he has sometimes been called the "father of science fiction", a title that has also been given to Jules Verne and Hugo Gernsback. In addition to his fame as a writer, he was prominent in his lifetime as a forward-looking, even prophetic social critic who devoted his literary talents to the development of a progressive vision on a global scale. As a futurist, he wrote a number of utopian works and foresaw the advent of aircraft, tanks, space travel, nuclear weapons, satellite television and something resembling the World Wide Web. His science fiction imagined time travel, alien invasion, invisibility, and biological engineering before these subjects were common in the genre. Brian Aldiss referred to Wells as the "Shakespeare of science fiction", while Charles Fort called him a "wild talent". Wells rendered his works convincing by instilling commonplace detail alongside a single extraordinary assumption per work – dubbed "Wells's law" – leading Joseph Conrad to hail him in 1898 with "O Realist of the Fantastic!". His most notable science fiction works include The Time Machine (1895), which was his first novella, The Island of Doctor Moreau (1896), The Invisible Man (1897), The War of the Worlds (1898), the military science fiction The War in the Air (1907), and the dystopian When the Sleeper Wakes (1910). Novels of social realism such as Kipps (1905) and The History of Mr Polly (1910), which describe lower-middle-class English life, led to the suggestion that he was a worthy successor to Charles Dickens, but Wells described a range of social strata and even attempted, in Tono-Bungay (1909), a diagnosis of English society as a whole. Wells was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature four times. Wells's earliest specialised training was in biology, and his thinking on ethical matters took place in a Darwinian context. He was also an outspoken socialist from a young age, often (but not always, as at the beginning of the First World War) sympathising with pacifist views. In his later years, he wrote less fiction and more works expounding his political and social views, sometimes giving his profession as that of journalist. Wells was a diabetic and co-founded the charity The Diabetic Association (Diabetes UK) in 1934.

4. Charles Dickens (1812 - 1870)
With an HPI of 85.20, Charles Dickens is the 4th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 169 different languages.
Charles John Huffam Dickens ( ; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime and, by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are widely read today. Born in Portsmouth, Dickens left school at age 12 to work in a boot-blacking factory when his father John was incarcerated in a debtors' prison. After three years, he returned to school before beginning his literary career as a journalist. Dickens edited a weekly journal for 20 years; wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and nonfiction articles; lectured and performed readings extensively; was a tireless letter writer; and campaigned vigorously for children's rights, education and other social reforms. Dickens's literary success began with the 1836 serial publication of The Pickwick Papers, a publishing phenomenon—thanks largely to the introduction of the character Sam Weller in the fourth episode—that sparked Pickwick merchandise and spin-offs. Within a few years, Dickens had become an international literary celebrity, famous for his humour, satire and keen observation of character and society. His novels, most of them published in monthly or weekly instalments, pioneered the serial publication of narrative fiction, which became the dominant Victorian mode for novel publication. Cliffhanger endings in his serial publications kept readers in suspense. The installment format allowed Dickens to evaluate his audience's reaction, and he often modified his plot and character development based on such feedback. For example, when his wife's chiropodist expressed distress at the way Miss Mowcher in David Copperfield seemed to reflect her own disabilities, Dickens improved the character with positive features. His plots were carefully constructed and he often wove elements from topical events into his narratives. Masses of the illiterate poor would individually pay a halfpenny to have each new monthly episode read to them, opening up and inspiring a new class of readers. His 1843 novella A Christmas Carol remains especially popular and continues to inspire adaptations in every creative medium. Oliver Twist and Great Expectations are also frequently adapted and, like many of his novels, evoke images of early Victorian London. His 1853 novel Bleak House, a satire on the judicial system, helped support a reformist movement that culminated in the 1870s legal reform in England. A Tale of Two Cities (1859; set in London and Paris) is regarded as his best-known work of historical fiction. The most famous celebrity of his era, he undertook, in response to public demand, a series of public reading tours in the later part of his career. The term Dickensian is used to describe something that is reminiscent of Dickens and his writings, such as poor social or working conditions, or comically repulsive characters.
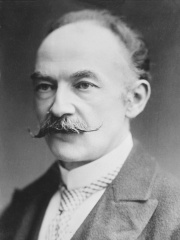
5. Thomas Hardy (1840 - 1928)
With an HPI of 84.42, Thomas Hardy is the 5th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 89 different languages.
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wordsworth. He was highly critical of much in Victorian society, especially on the declining status of rural people in Britain such as those from his native South West England. While Hardy wrote poetry throughout his life and regarded himself primarily as a poet, his first collection was not published until 1898. Initially, he gained fame as the author of novels such as Far from the Madding Crowd (1874), The Mayor of Casterbridge (1886), Tess of the d'Urbervilles (1891) and Jude the Obscure (1895). During his lifetime, Hardy's poetry was acclaimed by younger poets (particularly the Georgians) who viewed him as a mentor. After his death his poems were lauded by Ezra Pound, W. H. Auden and Philip Larkin. Many of his novels concern tragic characters struggling against their passions and social circumstances, and they are often set in the semi-fictional region of Wessex; initially based on the medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom, Hardy's Wessex eventually came to include the counties of Dorset, Wiltshire, Somerset, Devon, Hampshire and much of Berkshire, in south-west and south central England. Two of his novels, Tess of the d'Urbervilles and Far from the Madding Crowd, were listed in the top 50 on the BBC's survey of best-loved novels, The Big Read.

6. Arthur Conan Doyle (1859 - 1930)
With an HPI of 83.22, Arthur Conan Doyle is the 6th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 120 different languages.
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for A Study in Scarlet, the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Holmes and Dr. Watson. The Sherlock Holmes stories are milestones in the field of crime fiction. Doyle was a prolific writer. In addition to the Holmes stories, his works include fantasy and science fiction stories about Professor Challenger, and humorous stories about the Napoleonic soldier Brigadier Gerard, as well as plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction, and historical novels. One of Doyle's early short stories, "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement" (1884), helped to popularise the mystery of the brigantine Mary Celeste, found drifting at sea with no crew member aboard.

7. Lord Byron (1788 - 1824)
With an HPI of 82.84, Lord Byron is the 7th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 152 different languages.
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), was an English poet. He was one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest British poets. Among his best-known works are the lengthy narratives Don Juan and Childe Harold's Pilgrimage; many of his shorter lyrics in Hebrew Melodies also became popular. Byron was educated at Trinity College at the University of Cambridge. Following graduation, he travelled extensively in Europe, living for seven years in Italy, in Venice, Ravenna, Pisa, and Genoa, and then was forced to flee to England after receiving threats of lynching. During his stay in Italy, he would frequently visit his friend and fellow poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Later in life, Byron joined the Greek War of Independence to fight the Ottoman Empire, for which Greeks revere him as a folk hero. He died leading a campaign in 1824, at the age of 36, from a fever contracted after the first and second sieges of Missolonghi.

8. D. H. Lawrence (1885 - 1930)
With an HPI of 82.80, D. H. Lawrence is the 8th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 76 different languages.
David Herbert Lawrence (11 September 1885 – 2 March 1930) was an English novelist, short story writer, poet, playwright, literary critic, travel writer, essayist, and painter. His modernist works reflect on modernity, social alienation and industrialisation, while championing sexuality, vitality and instinct. Four of his most famous novels – Sons and Lovers (1913), The Rainbow (1915), Women in Love (1920), and Lady Chatterley's Lover (1928) – were the subject of censorship trials for their radical portrayals of romance, sexuality and use of explicit language. Lawrence's opinions and artistic preferences earned him a controversial reputation; he endured persecution and the misrepresentation of his creative work throughout his life, much of which he spent in a voluntary exile that he described as a "savage enough pilgrimage". At the time of his death, he had been variously scorned as tasteless, avant-garde, and a pornographer who had only garnered success for erotica; however, the English novelist and critic E. M. Forster, in an obituary notice, challenged this widely held view, describing him as "the greatest imaginative novelist of our generation". Later, the English literary critic F. R. Leavis also championed both his artistic integrity and his moral seriousness.

9. Daniel Defoe (1660 - 1731)
With an HPI of 82.76, Daniel Defoe is the 9th most famous British Writer. His biography has been translated into 102 different languages.
Daniel Defoe ( c. 1660 – 24 April 1731) was an English writer, merchant and spy. He is most famous for his novel Robinson Crusoe, published in 1719, which is claimed to be second only to the Bible in its number of translations. He has been seen as one of the earliest proponents of the English novel, and helped to popularise the form in Britain with others such as Aphra Behn and Samuel Richardson. Defoe wrote many political tracts, was often in trouble with the authorities, and spent a period in prison. Intellectuals and political leaders paid attention to his fresh ideas and sometimes consulted him. Defoe was a prolific and versatile writer, producing more than three hundred works—books, pamphlets, and journals—on diverse topics, including politics, crime, religion, marriage, psychology and the supernatural. He was also a pioneer of business journalism and economic journalism.

10. Virginia Woolf (1882 - 1941)
With an HPI of 81.81, Virginia Woolf is the 10th most famous British Writer. Her biography has been translated into 115 different languages.
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; née Stephen; 25 January 1882 – 28 March 1941) was an English writer and one of the most influential 20th-century modernist authors. She helped to pioneer the use of stream of consciousness narration as a literary device. Virginia Woolf was born in South Kensington, London, into an affluent and intellectual family as the seventh child of Julia Prinsep Jackson and Leslie Stephen. She grew up in a blended household of eight children, including her sister, the painter Vanessa Bell. Educated at home in English classics and Victorian literature, Woolf later attended King’s College London, where she studied classics and history and encountered early advocates for women’s rights and education. After the death of her father in 1904, Woolf and her family moved to the bohemian Bloomsbury district, where she became a founding member of the influential Bloomsbury Group. She married Leonard Woolf in 1912, and together they established the Hogarth Press in 1917, which published much of her work. They eventually settled in Sussex in 1940, maintaining their involvement in literary circles throughout their lives. Woolf began publishing professionally in 1900 and rose to prominence during the interwar period with novels like Mrs Dalloway (1925), To the Lighthouse (1927), and Orlando (1928), as well as the feminist essay A Room of One’s Own (1929). Her work became central to 1970s feminist criticism and remains influential worldwide, having been translated into over 50 languages. Woolf’s legacy endures extensive scholarship, cultural portrayals, and tributes such as memorials, societies, and university buildings bearing her name.
People
Pantheon has 789 people classified as British writers born between 518 and 1994. Of these 789, 200 (25.35%) of them are still alive today. The most famous living British writers include Anna Wintour, J. K. Rowling, and Jane Hawking. The most famous deceased British writers include William Shakespeare, Agatha Christie, and H. G. Wells. As of April 2024, 27 new British writers have been added to Pantheon including Simon Beckett, Edward St Aubyn, and Tom Parker Bowles.
Living British Writers
Go to all RankingsAnna Wintour
1949 - Present
HPI: 78.83
J. K. Rowling
1965 - Present
HPI: 76.63
Jane Hawking
1944 - Present
HPI: 74.68
Ken Follett
1949 - Present
HPI: 73.12
Julian Barnes
1946 - Present
HPI: 69.11
James May
1963 - Present
HPI: 68.92
Ian McEwan
1948 - Present
HPI: 68.84
David Irving
1938 - Present
HPI: 68.54
Philip Pullman
1946 - Present
HPI: 68.28
Len Deighton
1929 - Present
HPI: 67.44
Sarah, Duchess of York
1959 - Present
HPI: 66.96
E. L. James
1963 - Present
HPI: 65.78
Deceased British Writers
Go to all RankingsWilliam Shakespeare
1564 - 1616
HPI: 92.59
Agatha Christie
1890 - 1976
HPI: 85.80
H. G. Wells
1866 - 1946
HPI: 85.76
Charles Dickens
1812 - 1870
HPI: 85.20
Thomas Hardy
1840 - 1928
HPI: 84.42
Arthur Conan Doyle
1859 - 1930
HPI: 83.22
Lord Byron
1788 - 1824
HPI: 82.84
D. H. Lawrence
1885 - 1930
HPI: 82.80
Daniel Defoe
1660 - 1731
HPI: 82.76
Virginia Woolf
1882 - 1941
HPI: 81.81
Jane Austen
1775 - 1817
HPI: 80.62
Lewis Carroll
1832 - 1898
HPI: 80.04
Newly Added British Writers (2025)
Go to all RankingsSimon Beckett
1960 - Present
HPI: 54.38
Edward St Aubyn
1960 - Present
HPI: 49.63
Tom Parker Bowles
1974 - Present
HPI: 46.82
Siobhan Dowd
1960 - 2007
HPI: 46.65
Simon Sinek
1973 - Present
HPI: 45.25
Edward Lucas
1962 - Present
HPI: 43.36
Adrian Tchaikovsky
1972 - Present
HPI: 43.18
Ngarmpun Vejjajiva
1963 - Present
HPI: 42.63
A. L. Kennedy
1965 - Present
HPI: 42.19
Philip Ball
1962 - Present
HPI: 41.79
Ruth Ware
1977 - Present
HPI: 41.38
Samantha Harvey
1975 - Present
HPI: 41.35
Overlapping Lives
Which Writers were alive at the same time? This visualization shows the lifespans of the 25 most globally memorable Writers since 1700.



























